Northern lights will be visible in fewer states than originally forecast. Will you still be able to see them?
The northern lights are expected to be visible on Thursday, July 13 – but in fewer places than originally forecast.
The aurora borealis on these days will be "active," according to University of Alaska's Geophysical Institute, which initially predicted activity would be high.
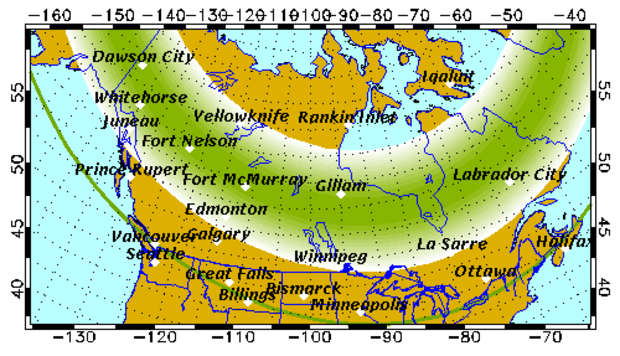
Weather permitting, parts of Alaska, South Dakota, Wisconsin, Michigan and Maine, as well as parts of Canada, are expected to see the northern lights on Thursday. The same states had been expected to see the lights on Wednesday as well.
Last week, the institute projected the display would be visible in 17 states over those two days: Washington, Iowa, Illinois, Ohio and Massachusetts on July 12, and Alaska, Montana, Minnesota, Wisconsin, Michigan, Oregon, Idaho, Wyoming, Nebraska, Indiana, Vermont and Maryland on July 13.
The institute told CBS News it originally predicted a moderate solar storm – which causes the dazzling phenomenon.
"The features on the sun that produce activity like this typically last 1-3 months, so the active conditions were predicted to occur again this week," a representative for the institute told CBS News via email. "However, now that the forecast activity is less than three days in the future, we can see that the solar features that produced the prior activity have actually diminished over the last month. This means that the high levels of activity previously expected are now considered much less likely."
NOAA also initially predicted high activity for this week and then downgraded their forecast. Solar wind from coronal holes in the sun flow towards Earth and have a magnetic reaction that causes the northern lights, also called the aurora borealis, according to NASA.
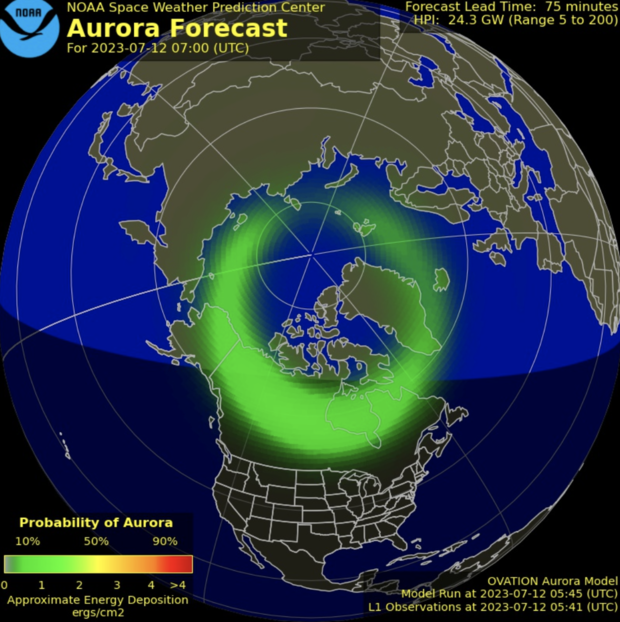
Bryan Brasher, a project manager at NOAA's Space Weather Prediction Center told CBS News one coronal hole in particular had previously shown elevated activity, so forecasters expected it to do so again.
"As this particular coronal hole rotated back into view – meaning we could see and analyze it – it was clear that it had diminished and we adjusted our forecast accordingly," Brasher told CBS News via email.
The scale for measuring these geomagnetic storms is called "the G scale," ranging from a minor storm at G1 to an extreme storm at G5. The original forecast that garnered media attention was at a G2, but NOAA recently lowered the forecast to a G1 and then lowered it again below the G scale, Brasher said.
Brasher said a G3 or a G4 storm would be needed to see the Northern Lights from mid-latitude states. "We did - for example - have a G4 storm in late March and again in late April that caused the aurora to be visible as far south as Arizona and Oklahoma," he said.
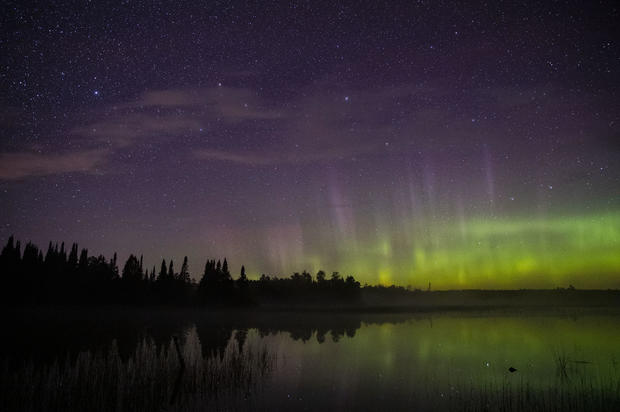

The best time to see the lights is when the sky is clear and dark, according to the institute. They are more visible closest to the equinox, or the longest days of sunlight in the year occurring in the spring and fall. Auroras come from solar storms.
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration has an animated forecast of the lights' movement and says the best time to see them is within an hour or two of midnight, usually between 10 p.m. and 2 a.m. local time.
During average activity, the lights are usually visible in Alaska, Canada, and Scandinavian countries like Greenland and Iceland during average activity and from late February to early April is usually the best time to view them in Alaska.
- In:
- Aurora Borealis
- Northern Lights

Caitlin O'Kane is a digital content producer covering trending stories for CBS News and its good news brand, The Uplift.
Disclaimer: The copyright of this article belongs to the original author. Reposting this article is solely for the purpose of information dissemination and does not constitute any investment advice. If there is any infringement, please contact us immediately. We will make corrections or deletions as necessary. Thank you.





