Onshore Wind Is Poised to Grow, and Move Away from Boom and Bust Cycles
Onshore wind energy is working on a comeback in the U.S. market.
This is odd to say considering that land-based wind farms are the country’s leading source of renewable power. But it reflects a market in which utility-scale solar and battery storage are growing at much faster rates, and offshore wind is on the cusp of substantial growth.
At the same time, onshore wind suffered through a rough 2022. The industry had 8.5 gigawatts of new projects go online last year, which was the lowest number since 2018 and less than half of the record high from 2020. Wind energy manufacturers felt the pain from this downturn, with layoffs and financial losses.
But the industry is now shifting back into growth mode thanks in part to tax credits under the Inflation Reduction Act, said Ryan Wiser, a senior scientist at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory.
“The signs for long-term growth are mostly positive,” he said.
I spoke with him about the 17th annual edition of Lawrence Berkeley’s wind energy market report, released this month. Wiser has been a co-author since the report’s inception, covering a period when the wind industry went from through its initial breakthrough in the 2000s and then matured into a major part of the energy economy in the 2010s.
Wind energy is now an essential part of the grid, and a difference-maker during periods of high demand due to extreme heat or cold. From January to May, wind farms generated 12.4 percent of U.S. electricity, nearly double the output of hydropower and more than triple that of utility-scale solar, according to the Energy Information Administration.
The wind industry suffered in 2022 because of difficulty obtaining parts, which affected many sectors, and because it was going through the trough of a boom and bust cycle tied to tax credits.
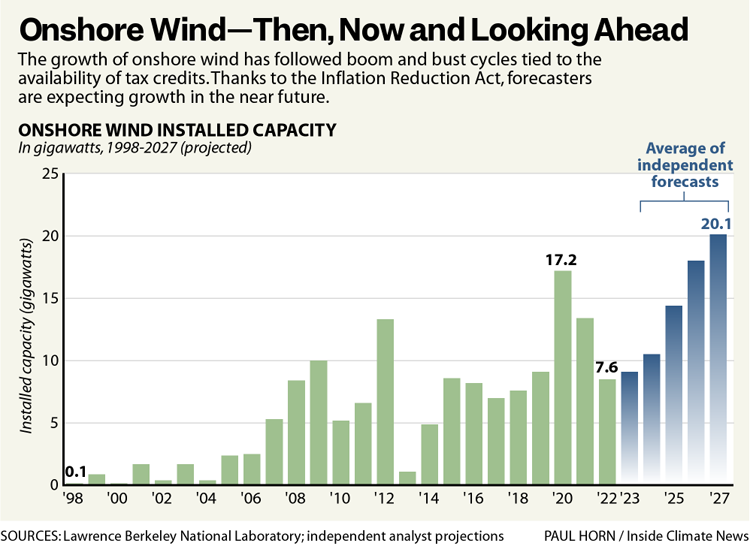
When you look at a chart of onshore wind energy capacity by year, the booms and busts are clear, as developers have rushed to build projects in time to get the best deal. But the credits have never gone away for long, with Congress approving several extensions.
The most recent peak was in 2020 with the completion of 17.2 gigawatts of onshore wind projects, just ahead of a phaseout of the production tax credit. Texas led the country in wind development, then and now.
The booms and busts have undermined the wind industry’s stability, leading to a need to ramp up hiring, followed by periods of retrenchment in jobs and investment.
The Inflation Reduction Act was designed to provide some relief from these ups and downs, with a production tax credit that will have the same rate until a phasedown begins in 2033.
The credit gives an owner 2.75 cents for every kilowatt-hour a project generates in its first 10 years, if the project meets standards for wages and benefits. Developers have opportunities for additional credits by using parts that qualify as domestic content and for being in an “energy community.” (An energy community, as defined by the law, includes places with a history of employment in fossil fuel industries and higher unemployment than the U.S. average, and places with shuttered coal mines or coal-fired power plants.)
For large wind farms, the credits can be worth tens of millions of dollars per year and make the difference between the project happening or not.
In recent months, there have been at least 11 announcements of plant openings, reopenings or expansions, leading to the addition of more than 3,000 jobs, the Lawrence Berkeley report says.
This growth is substantial, but it’s less than what’s happening in the supply chains for solar and batteries, which are benefiting from some of the same IRA provisions.
Wiser said some perspective is needed to understand that onshore wind energy is growing and an important part of the clean energy economy, while also acknowledging that its growth rate is not as high as other technologies. (Solar is on track to overtake onshore wind as the country’s leading source of renewable energy generation, but it still has a long way to go.)
Wind power is a more established technology, having been a major part of the market for more than a decade. Solar has emerged more recently as its costs dropped to the point that it became competitive with wind in much of the country.
The onshore wind industry has done most of its development in a band of states that run through the center of the country, from North Dakota and Minnesota in the north, to Texas in the south. These are the places with the strongest wind resources.
Solar is more versatile and able to be built profitably in more places, Wiser said.
Samantha Woodworth, a senior analyst at the research firm Wood Mackenzie, said onshore wind faces a high degree of difficulty in getting built compared to solar.
“Frankly, wind takes up loads more space and time to develop, and while the output is generally lower cost than solar, getting wind built is becoming more difficult as the optimal locations are taken up and developers have to look to other locations that are closer to population centers or with less good wind resources,” she said.
She sees optimism in the onshore wind industry because of the IRA, with the caveat that some details are still not clear because the government hasn’t finished writing rules for the tax credits. The final details on the rules, including the conditions for parts qualifying as domestic content, are important for determining the extent of the benefits for manufacturers and their customers.
Regardless of how much the tax credits stimulate the market, it will take some time for the policies to translate into projects.
The Lawrence Berkeley report cites forecasts from five sources, including Wood Mackenzie. The average of the forecasts is 9.1 gigawatts of new projects completed in 2023, which would be a small increase from 2022.
But the key point is the ensuing trend line. The annual total would increase each year, to 20.1 gigawatts in 2027, showing that this technology has a lot of life left in it.
Other stories about the energy transition to take note of this week:
First U.S. Offshore Wind Auction in the Gulf of Mexico Attracts Paltry Interest: There was no bidding war in the first federal auction for offshore wind development rights in the Gulf of Mexico. RWE, a German energy company, was the sole bidder and the winner with a $5.6 million bid, as Nichola Groom reports for Reuters. The RWE bid was for an area off of Louisiana. Two other areas, both off of Texas, received no bids. The Gulf’s lower wind speeds and soft soils may help to explain the lack of interest. This is in contrast with bidding in the Northeast, which attracted vigorous competition. One difference is that several states in that region have goals or requirements for developing offshore wind, while the Gulf states do not. Still, RWE thinks it got a bargain, and said its winning bid provides “a great opportunity to enter the Gulf’s offshore wind industry at the ground floor.”
Hourly Workers at GM Joint Venture Battery Plant in Ohio Negotiate a Wage Increase: Union workers at the Ultium Cells battery plant in Lordstown, Ohio, have ratified a contract that will give them a pay raise averaging 25 percent. Ultium is a joint venture of General Motors and LG Energy that makes EV batteries, and negotiations over the contract are part of a larger debate over whether workers at battery joint ventures will have wages and benefits similar to other unionized auto workers, as Jamie L. LaReau reports for the Detroit Free Press. United Auto Workers leaders have argued that joint venture employees should be part of the larger contract that includes Ford, GM and Stellantis. The Ultium contract was ratified at a time of high tension for labor relations in the auto industry, as the contract for those three major automakers is set to expire on Sept. 14.
Wyoming Could Gain the Most from Federal Climate Funding, But Obstacles Are Many: Wyoming is well-positioned to rake in substantial benefits from the Inflation Reduction Act, if the state can find a way to work through local opposition to clean energy projects and an affinity for fossil fuels, as my colleague Marianne Lavelle reports for ICN. The state is the leading coal producer in the United States, but it also has vast areas of land that are well-suited to developing renewable energy, like the acreage being used for the 3,500-megawatt Chokecherry and Sierra Madre Wind Energy Project, which is under construction. Any development is going to need to win support from local communities that aren’t used to renewable energy, and it will have to be done in a way that is respectful of concerns of environmental advocates who worry about changes to landscapes and ecosystems.
Utility Efficiency Spending Falls, Leading to 5.4 Percent Drop in Energy Savings: Electricity utility programs to help consumers reduce energy use have stagnated, according to a new report from the American Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy. The group says savings from the programs declined by 5.4 percent from 2018 to 2021, largely due to utilities reducing funding, as Robert Walton reports for Utility Dive. The programs have included rebates for insulation, appliance replacement and conversion to highly efficient lighting. I’m not surprised to see the decrease in savings, having covered the reductions in utility programs as they were happening. The companies successfully argued to regulators and lawmakers that energy efficiency spending should not be a high priority. Advocates for conservation are left to find other ways to help consumers reduce energy waste.
Inside Clean Energy is ICN’s weekly bulletin of news and analysis about the energy transition. Send news tips and questions to dan.gearino@insideclimatenews.org.
Disclaimer: The copyright of this article belongs to the original author. Reposting this article is solely for the purpose of information dissemination and does not constitute any investment advice. If there is any infringement, please contact us immediately. We will make corrections or deletions as necessary. Thank you.







